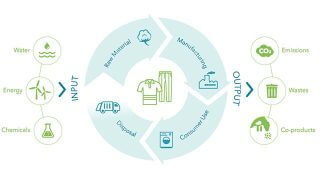
Circularity of Cotton
Cotton Circularity
Cotton is a naturally circular textile, and can be reused, recycled**, and returned∞ to the earth. Explore these three intersecting paths of cotton’s circular lifecycle and start envisioning your opportunities.
Circular Lifecycle of Cotton
Choose a product pathway to explore the many ways you can close the loop with cotton.

The U.S. cotton industry has set meaningful 10-year goals to guide scientifically sound, national-scale improvement over time.
Learn more about industry goals for sustainable cotton production.Download the Brochure
COTTON’S CIRCULAR LIFECYCLE
Grow your opportunities to advance the circular economy.
You know cotton as comfortable, durable, and incredibly versatile—a natural fiber you can use in products as wide-ranging as shirts, sheets, wet wipes, and 3D printed buttons.
Cotton can also be reused, recycled**, and returned∞ to the earth. So whatever product you make, there’s a circular path ahead when you make it with cotton.
Download our Cotton’s Circular Lifecycle brochure.
Cotton Sugar: An Environmentally Friendly Alternative
Matt Farrell, Textile Chemistry Research Manager at Cotton Incorporated, is dedicated to sustainable initiatives in the cotton industry, focusing on innovative solutions for the end-of-life phase of cotton. His research explores the transformative process of circular cotton – converting cotton textile waste into glucose, commonly known as sugar.
This unique approach opens up possibilities for repurposing cotton waste into bio-based chemicals, which are used in everyday products like detergents and cosmetics. This initiative not only extends the usability of cotton but could also contribute to more circularity in the textile industry.